Law's Interplay with Society and Public Life
Law serves as a fundamental pillar in the structure and function of human societies, providing the essential frameworks that govern interactions, protect rights, and maintain order. It is an intricate system of rules, principles, and institutions designed to regulate behavior, resolve disputes, and promote collective well-being. From the daily routines of individuals to the complex operations of governments and international bodies, the influence of legal concepts is pervasive, shaping public life and ensuring a degree of predictability and fairness in an ever-evolving world.

Legal Frameworks and Societal Order
The foundation of any organized society rests upon its legal frameworks. These systems are not merely collections of rules but comprehensive structures that define acceptable conduct, establish responsibilities, and outline the consequences of non-compliance. They encompass various branches of law, including civil, criminal, administrative, and international law, each addressing specific aspects of human activity. The primary objective of these frameworks is to foster societal order, providing a predictable environment where individuals and institutions can interact with a common understanding of their rights and obligations. Without such established systems, societies would struggle to resolve conflicts peacefully, protect vulnerable populations, or pursue collective goals effectively.
Governance, Policy, and Public Life
Governance refers to the processes by which decisions are made and implemented, involving various actors including governments, organizations, and the public. Law plays a critical role in defining the scope and limits of governmental authority and in shaping public policy. Policy decisions, whether concerning healthcare, education, or environmental protection, are almost always enshrined in legislation and administration. This legal grounding ensures that policies are not arbitrary but are developed and executed according to established procedures, often with opportunities for citizen input and judicial review. The interplay between law, governance, and public life is dynamic, reflecting societal values and aspirations while providing the mechanisms for their realization.
Constitutional Rights and Citizen Protection
At the heart of many legal systems, particularly in democratic nations, are constitutional principles that safeguard fundamental rights. These constitutional documents establish the basic rules of governance and delineate the powers of the state while guaranteeing liberties to its citizens. Such rights often include freedom of speech, assembly, religion, and the right to due process. The judiciary plays a crucial role in interpreting these constitutional provisions and ensuring that legislation and governmental actions uphold these protections. This mechanism provides a vital check on state authority, reinforcing the principle that even governments are subject to law and must respect the inherent dignity and freedoms of their people.
Legislation, Statutes, and Regulatory Compliance
Legislation, enacted by legislative bodies, forms the bulk of a nation’s statutes and codified law. These statutes cover a vast array of subjects, from commerce and property to criminal offenses and public safety. Alongside legislation, regulation by governmental agencies provides detailed rules and standards necessary for the practical application of broader laws. Ensuring compliance with these regulations is a significant aspect of both public and private sector operations. Businesses, organizations, and individuals must navigate complex requirements to operate legally, contributing to consumer protection, environmental stewardship, and fair competition. The constant evolution of technology and societal challenges often necessitates new legislation and regulation to address emerging issues.
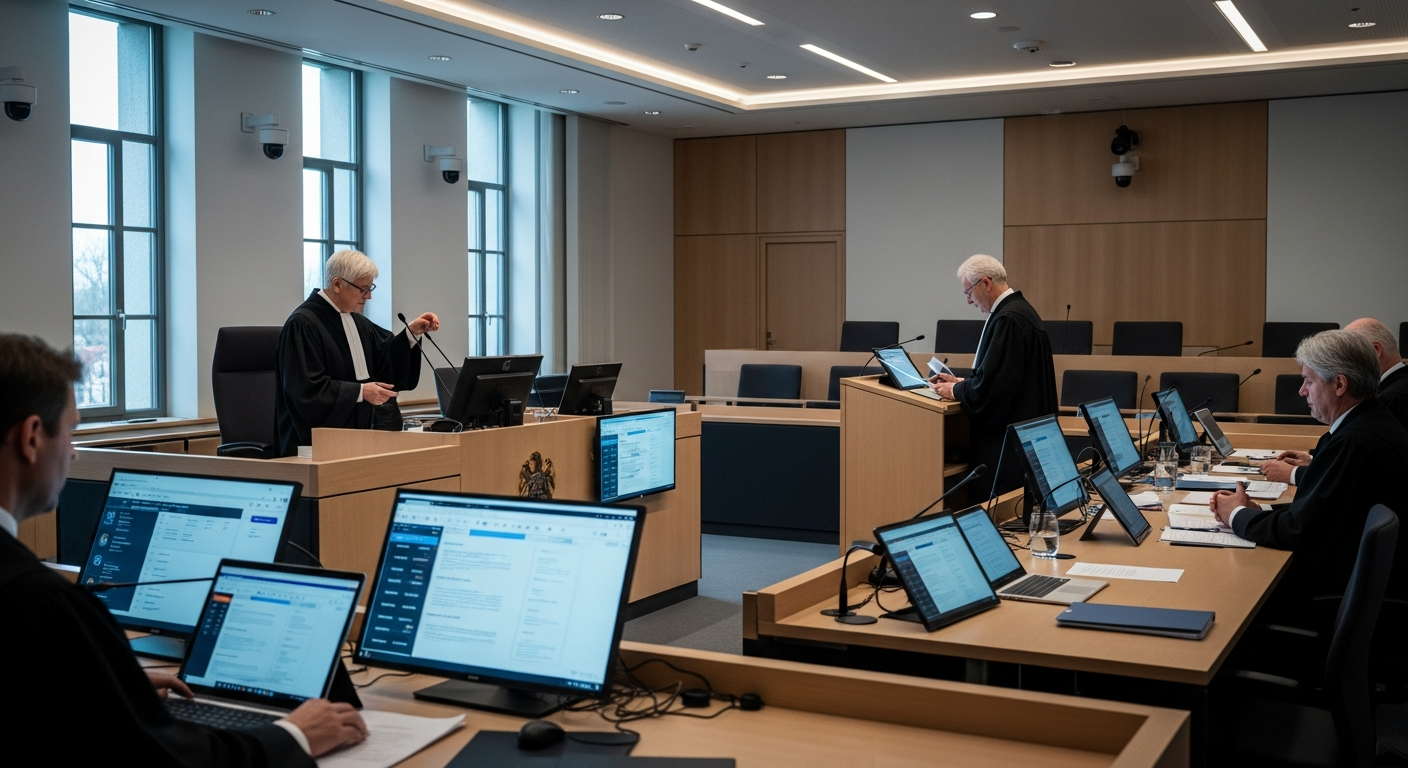
The Role of Justice and the Judiciary
Justice is a core concept that underpins the entire legal system, aiming for fairness, impartiality, and the equitable application of law. The judiciary, comprising courts and judges, is the branch of government responsible for interpreting and applying laws to specific cases, resolving disputes, and ensuring that justice is served. Through trials, hearings, and appeals, the judiciary upholds the rule of law, holds individuals and entities accountable, and protects rights. This independent role is crucial for maintaining public trust in the legal system and for providing a mechanism for redress when laws are violated or disputes arise. The principles of due process and equal protection under the law are central to the pursuit of justice.
Global Law and State Authority
In an increasingly interconnected world, global law plays a significant role in governing relations between nations and addressing issues that transcend national borders. This includes international treaties, conventions, and customary law that regulate areas such as human rights, trade, environmental protection, and armed conflict. While each state retains its sovereign authority, participation in international agreements often involves a commitment to adhere to global legal norms. The interplay between national legal systems and international law can be complex, often requiring states to harmonize their domestic legislation with their international obligations. This dimension of law highlights the broader implications of legal frameworks beyond individual nation-states, fostering cooperation and addressing challenges that require a collective response.
Law’s pervasive influence on society and public life is undeniable, shaping the fabric of our communities and guiding the interactions between individuals, organizations, and governments. From establishing fundamental rights and maintaining order to facilitating global cooperation, legal frameworks provide the essential structure for a functioning society. Understanding the various facets of law, including constitutional principles, legislation, regulation, and the role of the judiciary, offers insight into how societies strive for justice, governance, and the well-being of their citizens.