Kinetic Energy Recovery Systems: Powering the Future of Racing
The world of motorsport is constantly evolving, pushing the boundaries of automotive technology and performance. One innovation that has revolutionized racing in recent years is the Kinetic Energy Recovery System, or KERS. This cutting-edge technology has not only transformed the way race cars perform on the track but has also paved the way for advancements in road car efficiency and sustainability. In this article, we'll dive deep into the world of KERS, exploring its origins, functionality, and impact on the automotive industry.
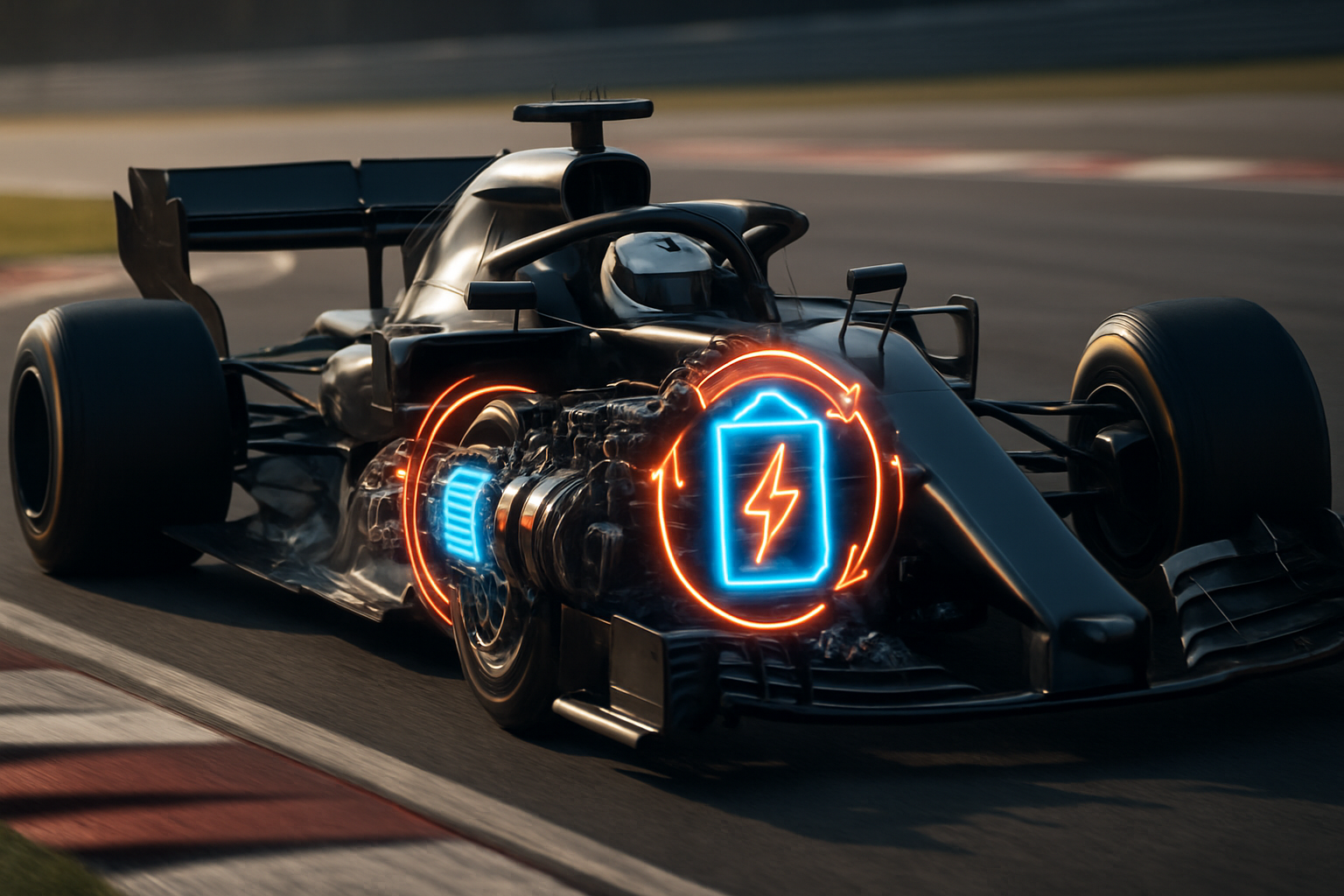

How KERS Works: Capturing and Deploying Energy
At its core, KERS is an ingenious method of capturing the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking. This energy is then stored and can be redeployed to provide an additional power boost when needed. There are two main types of KERS: electrical and mechanical. Electrical KERS uses a motor-generator unit connected to the drivetrain to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then stored in a battery. Mechanical KERS, on the other hand, stores energy in a flywheel system.
KERS in Formula 1: A Game-Changer on the Track
The introduction of KERS in Formula 1 in 2009 marked a significant milestone in racing technology. Initially, the system was optional, and teams could choose whether to implement it or not. However, it quickly became clear that KERS offered a substantial competitive advantage. The ability to deploy an additional 80 horsepower for up to 6.7 seconds per lap allowed drivers to make crucial overtaking maneuvers or defend their position more effectively.
Beyond Formula 1: KERS in Other Racing Series
The success of KERS in Formula 1 led to its adoption in other motorsport categories. Endurance racing series like the FIA World Endurance Championship and the 24 Hours of Le Mans embraced hybrid technologies, including more advanced energy recovery systems. These systems not only improved performance but also significantly enhanced fuel efficiency, allowing cars to complete longer stints between pit stops.
From Track to Street: KERS Technology in Road Cars
The development of KERS in motorsport has had a profound impact on the automotive industry as a whole. Many of the principles behind KERS have been adapted for use in road cars, particularly in the form of regenerative braking systems found in hybrid and electric vehicles. These systems help to improve overall efficiency and extend the range of electric vehicles, making them more practical for everyday use.
The Future of KERS: Innovations on the Horizon
As automotive technology continues to advance, so too does the potential for KERS. Engineers are exploring ways to make the systems more compact, efficient, and powerful. One area of particular interest is the development of supercapacitors, which could potentially store and release energy more quickly than current battery-based systems. Additionally, researchers are investigating the use of advanced materials like graphene to create more efficient and lightweight energy storage solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of KERS Technology
Despite its many advantages, KERS is not without its challenges. The added weight and complexity of the system can be a significant drawback, particularly in racing applications where every gram counts. There are also reliability concerns, as the high-stress environment of motorsport can put tremendous strain on KERS components. Furthermore, the cost of developing and implementing KERS technology remains a barrier for many smaller racing teams and car manufacturers.
The Environmental Impact of KERS
One of the most significant benefits of KERS technology is its potential to reduce the environmental impact of both racing and road cars. By capturing and reusing energy that would otherwise be wasted, KERS-equipped vehicles can achieve higher levels of efficiency and lower emissions. This aligns with the growing global focus on sustainability and the push towards greener transportation solutions.
KERS and the Evolution of Driver Skills
The introduction of KERS has not only changed the technology of racing but has also had a profound impact on driving techniques. Drivers must now master the art of energy management, deciding when to harvest energy and when to deploy it for maximum advantage. This adds an extra layer of strategy to racing, requiring drivers to think not just about their immediate performance but also about managing their energy resources throughout the entire race.
In conclusion, Kinetic Energy Recovery Systems represent a significant leap forward in automotive technology. From its origins in Formula 1 to its growing presence in road cars, KERS has demonstrated the potential to revolutionize the way we think about energy efficiency and performance in vehicles. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications that push the boundaries of what’s possible in both motorsport and everyday driving. The future of automotive engineering is undoubtedly electrifying, and KERS is at the forefront of this exciting revolution.