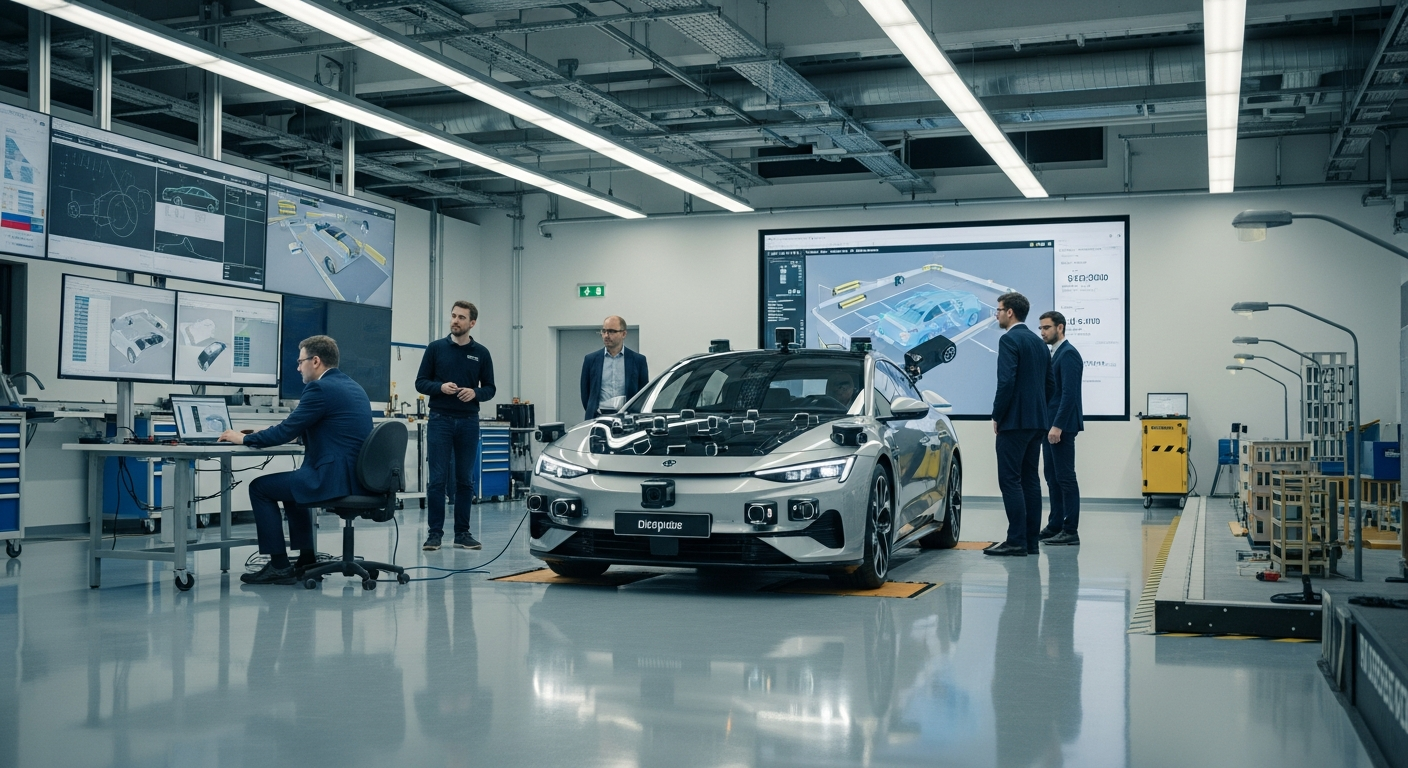
Decentralized Processing: The Rise of Edge Computing
The digital landscape is undergoing a significant transformation with the emergence of edge computing, a paradigm shift from traditional centralized data processing. This innovative approach brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data generation, rather than relying solely on distant cloud servers. By decentralizing processing, edge computing aims to reduce latency, conserve bandwidth, and enhance the efficiency and reliability of various digital services and applications across numerous industries worldwide.
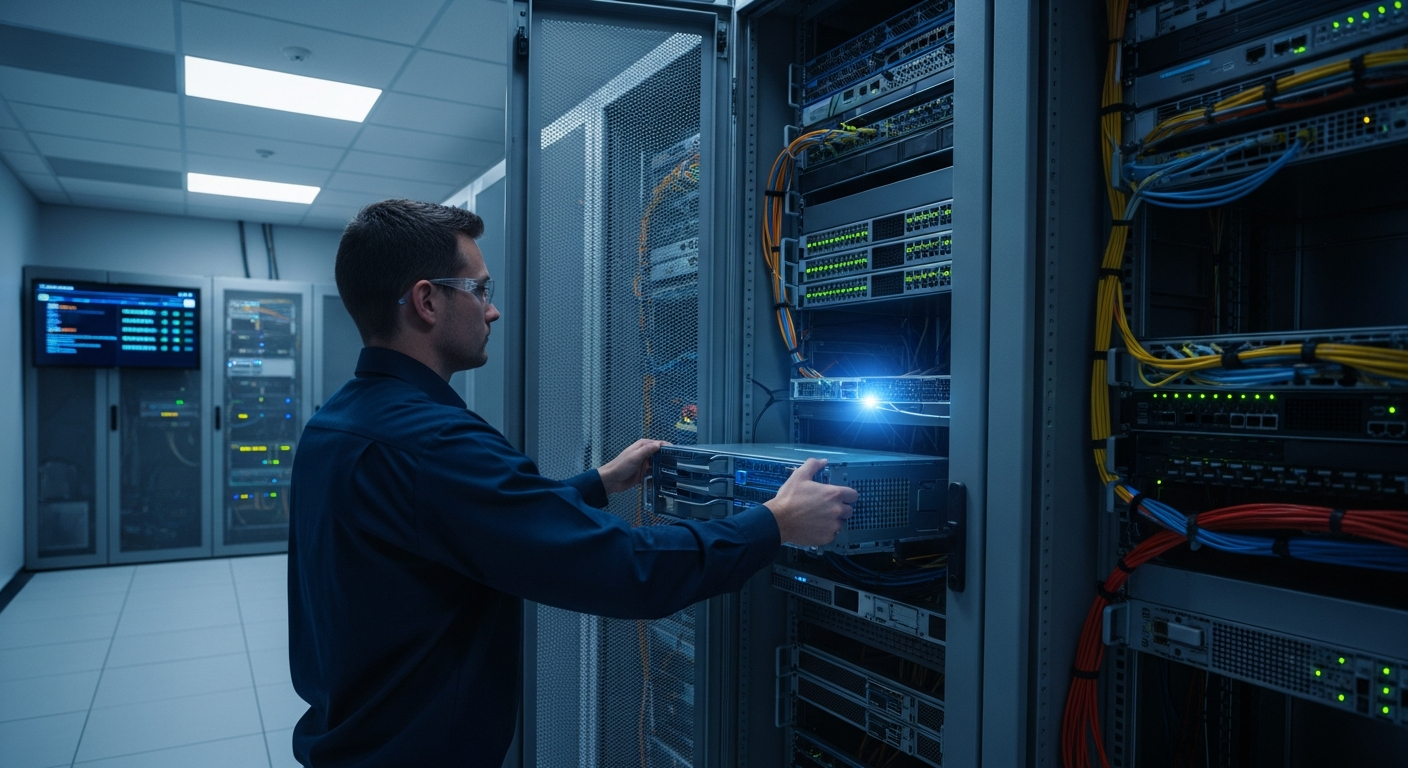

What is Edge Computing and How Does it Function?
Edge computing represents a distributed computing framework that moves computation and data storage from a central cloud or data center to the ‘edge’ of the network, where data is generated. This fundamental shift in computing architecture allows for data processing to occur in real-time or near real-time, directly at the source. For instance, instead of sending all raw data from an IoT device to a central server for analysis, edge computing enables immediate processing on the device itself or on a local server. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over long distances, thereby decreasing network congestion and improving response times for critical applications. The core idea is to process data as close as possible to where it is created, improving overall system performance and responsiveness.
The Role of Edge Devices and Hardware
The implementation of edge computing heavily relies on specialized electronics and hardware, commonly referred to as edge devices. These devices range from industrial sensors and smart cameras to autonomous vehicles and local servers located at the network’s periphery. Unlike traditional data centers, edge hardware is often designed to be robust, compact, and energy-efficient, capable of operating in diverse and sometimes challenging environments. The advancements in microprocessors, memory, and storage capabilities in these devices are crucial for handling the increasing volume and complexity of data generated at the edge. These devices are equipped to collect, filter, analyze, and even act upon data without constant reliance on a central cloud, making them pivotal for the digital transformation.
Enhancing Data Processing and Connectivity
One of the primary benefits of edge computing is its ability to significantly enhance data processing capabilities and optimize connectivity. By processing data locally, the need to transfer vast amounts of raw data to a central cloud is minimized. This not only reduces bandwidth consumption but also drastically cuts down on latency, which is critical for applications requiring immediate responses, such as autonomous driving, real-time industrial automation, and augmented reality. Improved connectivity at the edge ensures that devices can communicate efficiently with each other and with local servers, creating a more resilient and responsive network architecture. This decentralized processing model contributes to a more efficient use of network resources and a better user experience.
Innovations and Future Applications
Edge computing is a catalyst for numerous innovations, paving the way for advanced applications across various sectors. Its capabilities are particularly beneficial for integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models closer to data sources, enabling faster insights and automated decision-making. Imagine smart cities where traffic lights adapt in real-time based on local sensor data, or healthcare devices providing immediate diagnostic feedback. While quantum computing is still in its nascent stages, the principles of localized, high-speed processing could eventually intersect with edge paradigms, potentially enabling even more complex computations at the network’s periphery. The future of human-computer interaction, including sophisticated displays and immersive experiences, will also greatly benefit from the low-latency processing that edge computing provides.
Addressing Power and Security Challenges
While offering significant advantages, the widespread adoption of edge computing also presents challenges related to power management and security. Edge devices, often deployed in remote or resource-constrained locations, require efficient power solutions to ensure sustainability and continuous operation. Balancing computational power with energy consumption is a key design consideration for edge hardware. Furthermore, distributing data processing across numerous edge locations inherently expands the attack surface for cyber threats. Robust security measures, including strong encryption, authentication protocols, and continuous monitoring, are essential to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of edge systems. Developing comprehensive security frameworks that can scale across a diverse array of devices and environments is paramount for the successful deployment of edge technology.
Edge Computing Solutions and Providers
The edge computing market includes a range of solutions from various technology providers, encompassing hardware, software platforms, and integrated services. These offerings cater to different industry needs, from manufacturing and retail to telecommunications and smart infrastructure. Companies often provide specialized hardware tailored for edge deployments, alongside software platforms that facilitate application deployment, data management, and security at the edge. The ecosystem is dynamic, with ongoing development in areas like AI at the edge, real-time analytics, and enhanced connectivity options. Many providers also focus on developing tools that simplify the orchestration and management of distributed edge infrastructure, making it more accessible for businesses to implement these advanced systems.
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation (Monthly) |
|---|---|---|
| Edge Device Management Platform | AWS IoT Greengrass | Varies by usage, starting from free tier |
| Edge AI Development Kit | NVIDIA Jetson Series | Varies by model, hardware cost |
| Industrial Edge Gateway | Siemens Industrial Edge | Varies by specific model and software licenses |
| Edge Computing Software Stack | Microsoft Azure IoT Edge | Varies by usage and connected devices |
| Managed Edge Services | Google Cloud IoT Core | Varies by data ingress/egress and operations |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The Future of Decentralized Systems
Edge computing is reshaping how we conceive and implement digital systems. By bringing computing power closer to the data source, it addresses critical issues of latency, bandwidth, and reliability, paving the way for a new generation of smart, responsive, and efficient applications. As technology continues to evolve, with advancements in AI, materials science, and network connectivity, the capabilities of edge computing will only expand, further integrating digital intelligence into every aspect of our physical world. The paradigm of decentralized processing stands as a fundamental pillar in the ongoing evolution of global technology infrastructure, promising a more interconnected and instantaneous digital future.