Conservation Efforts: Protecting Endangered Animal Populations
The planet's rich biodiversity faces unprecedented challenges, with numerous animal species teetering on the brink of extinction. Conservation efforts are crucial for safeguarding these vulnerable populations and preserving the intricate balance of Earth's ecosystems. Understanding the threats and implementing effective strategies are vital steps toward ensuring a future where wildlife can thrive. This article explores the multifaceted approaches employed globally to protect endangered animals, highlighting the importance of collective action in maintaining ecological health.

Understanding Vulnerable Species and Their Habitats
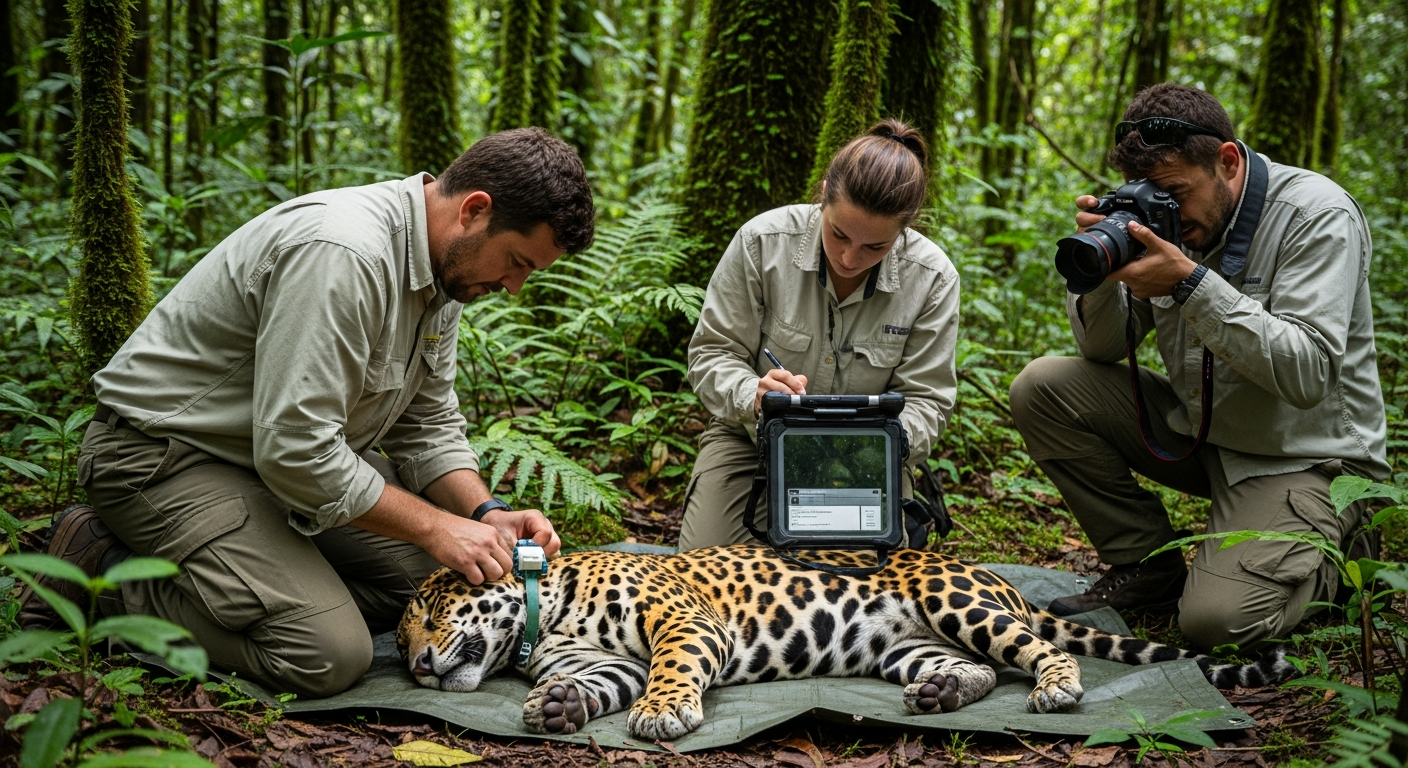
Protecting endangered animal populations begins with a thorough understanding of the species themselves and the unique habitats they rely upon. Many factors contribute to a species becoming endangered, including habitat loss, climate change, pollution, disease, and overhunting. Each species, whether a majestic large animal or a tiny insect, plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Scientists and conservationists meticulously study the behavior, instincts, and life cycles of these wildlife species to identify critical needs and vulnerabilities. This research informs targeted conservation strategies, ensuring efforts are tailored to the specific challenges faced by each population and their natural environments.
Effective conservation often requires identifying and preserving critical habitats. These areas are essential for feeding, breeding, and sheltering species. Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas are crucial steps in safeguarding these spaces from human development and exploitation. Beyond simple protection, habitat restoration projects aim to repair damaged ecosystems, reintroducing native plant species and improving water quality to create more viable environments for wildlife to flourish. Understanding the interconnectedness of all living things within these ecosystems is fundamental to successful long-term preservation.
Strategies for Wildlife Conservation and Rescue
Various strategies are employed worldwide to protect endangered animal populations. One significant approach is captive breeding programs, where species at high risk are bred in controlled environments with the goal of reintroducing them into the wild. These programs often involve careful management of genetics to maintain diversity and ensure the health of future generations. Rescue operations are also critical, particularly for individual animals or small groups affected by immediate threats like oil spills, natural disasters, or poaching. These rescued animals often receive specialized care and rehabilitation before potential release.
Technological advancements are increasingly aiding conservation efforts. Drones are used for monitoring remote wildlife populations and detecting illegal poaching activities. Satellite tracking provides invaluable data on animal movements and habitat use, helping to design more effective protected areas. Community involvement is another cornerstone of successful conservation, transforming local populations from potential threats into active partners. By providing education and economic alternatives to activities that harm wildlife, organizations foster a sense of shared responsibility and a deeper bond with nature.
The Role of Animal Welfare and Health in Preservation
Ensuring the welfare and health of endangered animal populations is paramount, whether they are in the wild or under human care. For wild populations, monitoring their health status can provide early warnings about environmental changes or disease outbreaks that could devastate a species. Veterinary expertise is often crucial in diagnosing and treating illnesses in rescued or captive animals, as well as in developing vaccination programs for certain diseases that threaten wildlife. Understanding animal behavior and providing appropriate enrichment in captive settings helps reduce stress and promotes natural instincts, which are vital for successful reintroduction into the wild.
Proper nutrition is another key aspect of animal welfare and health in conservation. For animals in captive breeding programs, carefully balanced diets are formulated to meet their specific needs, mimicking their natural food sources as closely as possible. In some cases, supplementary feeding may be necessary for wild populations during periods of extreme scarcity, though this is managed carefully to avoid dependency. The overall goal is to maintain robust, healthy populations that are resilient to environmental pressures and capable of reproducing naturally, contributing to the long-term survival of the species.
Global Cooperation and Community Engagement
Effective conservation of endangered animal populations requires a concerted global effort, transcending national borders and political differences. International agreements and treaties play a crucial role in coordinating actions to protect migratory species and combat illegal wildlife trade. Organizations worldwide collaborate on research, funding, and strategy development, sharing knowledge and resources to maximize impact. This global communication and cooperation are essential for addressing issues like climate change and transboundary pollution, which affect ecosystems across the planet.
Local communities are at the forefront of conservation efforts, often living alongside endangered wildlife. Engaging these communities through education, sustainable livelihood programs, and participatory management approaches is vital. When local populations understand the value of conservation and benefit from it, they become powerful advocates and guardians of their natural heritage. Fostering a strong bond between humans and animals at a local level contributes significantly to the broader goal of protecting species for future generations, ensuring the health and biodiversity of Earth’s ecosystems for all.
Protecting endangered animal populations is a complex but critical endeavor that demands continuous dedication and innovative solutions. From scientific research and habitat preservation to rescue operations and global cooperation, every effort contributes to the survival of vulnerable species and the health of our planet’s ecosystems. The future of wildlife hinges on the collective commitment to conservation, ensuring a diverse and thriving natural world for generations to come.